Boat battery corrosion can have far-reaching effects that impact your boat’s performance, your wallet, and the environment. If left unchecked, it leads to complications that every boater should be aware of. Here, we’re going into greater detail about the consequences of boat battery corrosion to help you stop it in its tracks and prevent it in the future.
What Causes Boat Battery Corrosion?
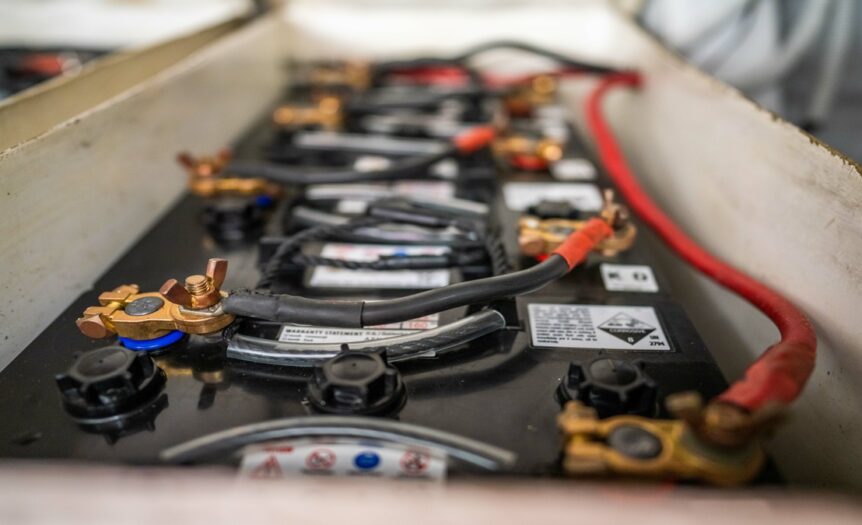
Battery corrosion typically results from chemical reactions occurring within or around the battery. Common culprits include exposure to saltwater, high humidity levels, and the gases released as batteries charge and discharge. For boaters in areas like Florida, with its warm and salty environment, these factors amplify the risk.
Corrosion often begins undetected. The terminals become coated with white or blue-green powder, which is a telltale sign of degraded materials. Over time, this damage spreads, resulting in reduced efficiency or even total battery failure. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward preventing the larger consequences of corrosion.
Harmful Effects on the Environment
When corroded batteries aren’t properly managed or disposed of, they wreak havoc on marine ecosystems. Corrosion often releases toxic chemicals and heavy metals, such as lead or acid, into the water. These pollutants harm fish, coral reefs, and other marine life that are vital for maintaining balanced and healthy waterways and oceans.
Economic Costs That Add Up
Battery corrosion leads to boat performance issues, such as compromised starting power or weak electric motors. For boaters who rely on electric engines, this means spending extra on battery replacements or costly repairs to circuits damaged by corrosion.
Beyond personal costs, boating professionals like fishing charters or tour operators may face cancellations and loss of income when their vessels are unexpectedly out of operation. Corrosion has financial ripple effects that affect your day-to-day boating activities—and who wants to lose money?
Proper Practices To Prevent Battery Corrosion
The best way to avoid these issues is to stay proactive. Regularly inspect your battery terminals and take preventative measures, such as applying anti-corrosion sprays or shields. Cleaning terminals with a mix of baking soda and water can neutralize acidic buildup and keep corrosion at bay.
Investing in high-quality marine-grade batteries also makes a big difference in their lifespan. Such batteries can withstand the damp, salty conditions common in boating environments. Proper storage, such as keeping batteries in a dry and ventilated compartment when not in use, minimizes exposure to corrosive elements.
Watch Out for Missteps With Electric Boat Motors
Boaters relying on electric motors must pay close attention to battery upkeep. Neglecting basic care, like failing to check terminals or overcharging batteries, exacerbates the risk of corrosion. Excessive charging releases more fumes, which leads to accelerated wear and increased maintenance costs. Additionally, ignoring potential corrosion around connectors may cause electric motors to run less efficiently, draining power and leaving you stranded when least expected.
Avoid common boat motor missteps by regularly monitoring battery health, charging them correctly, and using corrosion-resistant materials for connections. A little diligence goes a long way toward preserving power and ensuring smooth voyages.
Many boaters are unaware of how far-reaching the consequences of boat battery corrosion are until it’s too late. Whether it’s the harm it causes to marine life or the financial strain it places on your boating lifestyle, it’s clear that proper maintenance is nonnegotiable.










 Deering Estate
Deering Estate
 Massage Envy South Miami
Massage Envy South Miami
 Calla Blow Dry
Calla Blow Dry
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic
 Sushi Maki
Sushi Maki
 Sports Grill
Sports Grill
 The Healthy Kitchen
The Healthy Kitchen
 Golden Rule Seafood
Golden Rule Seafood
 Malanga Cuban Café
Malanga Cuban Café

 Kathleen Ballard
Kathleen Ballard
 Panter, Panter & Sampedro
Panter, Panter & Sampedro
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 The Dog from Ipanema
The Dog from Ipanema
 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic




 ATR Luxury Homes
ATR Luxury Homes


 2112 Design Studio
2112 Design Studio
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company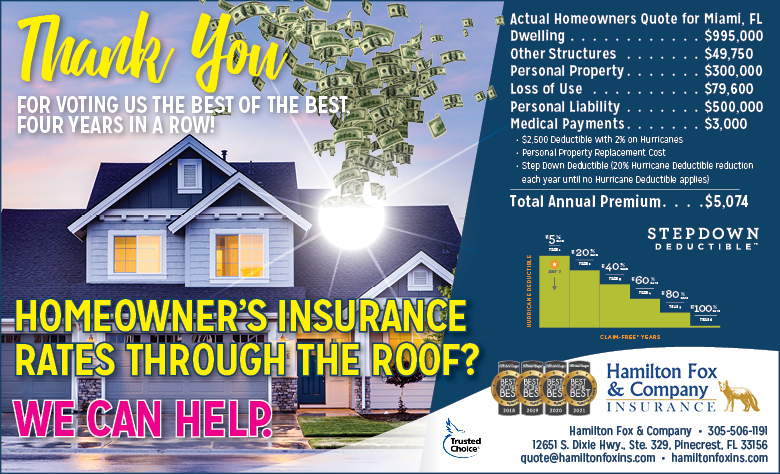
 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services
 Best Pest Professionals
Best Pest Professionals
 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Trinity Air Conditioning Company
Trinity Air Conditioning Company
 Cisca Construction & Development
Cisca Construction & Development
 Mosquito Joe
Mosquito Joe
 Cutler Bay Solar Solutions
Cutler Bay Solar Solutions


 Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
 Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
 Pineview Preschools
Pineview Preschools
 Westminster
Westminster
 Carrollton
Carrollton
 Lil’ Jungle
Lil’ Jungle
 Frost Science Museum
Frost Science Museum
 Palmer Trinity School
Palmer Trinity School
 South Florida Music
South Florida Music
 Pinecrest Orthodontics
Pinecrest Orthodontics
 Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
 d.pediatrics
d.pediatrics
 South Miami Women’s Health
South Miami Women’s Health

 The Spot Barbershop
The Spot Barbershop
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic




 Miami Dance Project
Miami Dance Project

 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic

 Safes Universe
Safes Universe
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 Evenings Delight
Evenings Delight





 Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
 Baptist Health South Florida
Baptist Health South Florida

 Laser Eye Center of Miami
Laser Eye Center of Miami
 Visiting Angels
Visiting Angels
 OpusCare of South Florida
OpusCare of South Florida

 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best





 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company


 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services