Milk plays a central role in many diets around the world, offering nutrition and versatility in cooking and consumption. While cow’s milk has long been the staple choice, evolving dietary preferences, health trends, and environmental consciousness have led to an increase in alternative milk sources. We’re exploring the different types of consumer milk sources, highlighting what they bring to the table.
The Basics of Cow’s Milk
Cow’s milk remains the primary choice for many households due to its nutritional balance and long-standing availability. Packed with essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and vitamin D, it’s ideal for supporting bone and muscle health. Full-fat, reduced-fat, and fat-free options cater to a range of dietary needs. Recently, lactose-free options have also addressed the needs of those with lactose intolerance, making cow’s milk more accessible.
Its neutral flavor profile makes it a favorite for use in beverages, cooking, and baking. From lattes to creamy pasta sauces, cow’s milk’s versatility solidifies its leadership among milk sources. However, concerns about the environmental impact of dairy farming have spurred interest in sustainable alternatives.
Why Goat’s Milk Stands Out
Goat’s milk, while less commonly consumed than cow’s milk, is a nutritionally rich option often hailed for its digestibility. It contains smaller fat globules, which may make it easier on the digestive system, particularly for individuals sensitive to cow’s milk. Slightly tangy and creamy, goat’s milk effortlessly lends itself to cheeses, yogurts, and various artisanal beverages.
Ethical considerations come into play when sourcing goat’s milk. Seeking knowledge about sustainable and humane farming practices can make the choice more responsible. Fun fact: learning everything to know about milking a goat reveals how hands-on and precise the milking process must be to ensure high-quality milk.
Almond Milk for Dairy-Free Lifestyles
Almond milk has surged in popularity as one of the most common plant-based milk alternatives. Made by blending almonds with water and straining out the solids, it’s inherently lactose-free, low in calories, and rich in vitamin E. Almond milk is particularly attractive to individuals seeking lighter, nutty-flavored options for smoothies, cereals, or even baking.
That said, almond milk may not pack the same protein punch as its dairy counterparts, so pairing it with a well-rounded diet is important. Sustainability concerns related to water usage during almond farming have raised questions about environmental impact, encouraging buyers to look for responsibly sourced options.
Soy Milk’s Nutritional Powerhouse
Soy milk, derived from soybeans, is another significant contender in the milk alternative market. Gaining popularity for being rich in protein, it rivals dairy milk in nutritional value. Additionally, fortified versions often provide calcium and vitamin D, making them strong replacements for cow’s milk, particularly in vegan diets.
Its bold, slightly bean-like flavor makes soy milk ideal for cooking and coffee, where it holds up to heat without curdling. Soy milk also carries certain health benefits, such as supporting heart health due to its isoflavones, compounds found in soy that contribute to cholesterol reduction.
Different types of milk sources provide an array of choices to suit the diverse preferences and dietary needs of today’s consumers. Whether you value the creaminess of goat’s milk, the versatility of cow’s milk, or the plant-based benefits of almond and soy milk, selecting the right option involves understanding your health priorities, ethical values, and taste preferences.










 Deering Estate
Deering Estate
 Massage Envy South Miami
Massage Envy South Miami
 Calla Blow Dry
Calla Blow Dry
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic
 Sushi Maki
Sushi Maki
 Sports Grill
Sports Grill
 The Healthy Kitchen
The Healthy Kitchen
 Golden Rule Seafood
Golden Rule Seafood
 Malanga Cuban Café
Malanga Cuban Café

 Kathleen Ballard
Kathleen Ballard
 Panter, Panter & Sampedro
Panter, Panter & Sampedro
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 The Dog from Ipanema
The Dog from Ipanema
 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic




 ATR Luxury Homes
ATR Luxury Homes


 2112 Design Studio
2112 Design Studio
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company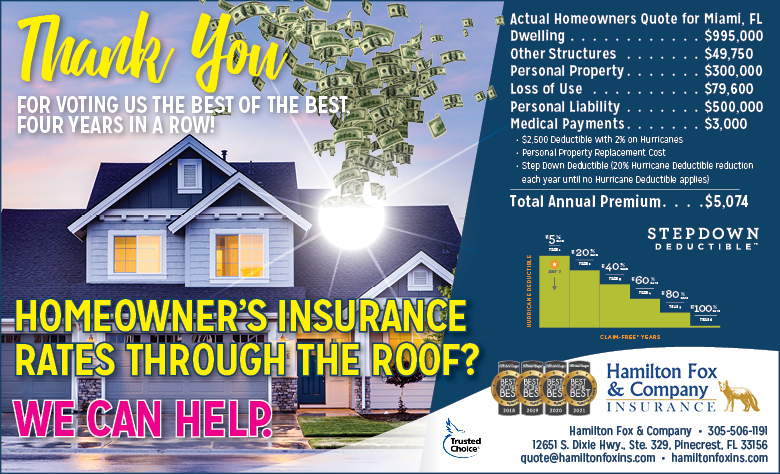
 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services
 Best Pest Professionals
Best Pest Professionals
 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Trinity Air Conditioning Company
Trinity Air Conditioning Company
 Cisca Construction & Development
Cisca Construction & Development
 Mosquito Joe
Mosquito Joe
 Cutler Bay Solar Solutions
Cutler Bay Solar Solutions


 Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
 Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
 Pineview Preschools
Pineview Preschools
 Westminster
Westminster
 Carrollton
Carrollton
 Lil’ Jungle
Lil’ Jungle
 Frost Science Museum
Frost Science Museum
 Palmer Trinity School
Palmer Trinity School
 South Florida Music
South Florida Music
 Pinecrest Orthodontics
Pinecrest Orthodontics
 Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
 d.pediatrics
d.pediatrics
 South Miami Women’s Health
South Miami Women’s Health

 The Spot Barbershop
The Spot Barbershop
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic




 Miami Dance Project
Miami Dance Project

 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic

 Safes Universe
Safes Universe
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 Evenings Delight
Evenings Delight





 Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
 Baptist Health South Florida
Baptist Health South Florida

 Laser Eye Center of Miami
Laser Eye Center of Miami
 Visiting Angels
Visiting Angels
 OpusCare of South Florida
OpusCare of South Florida

 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best





 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company


 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services