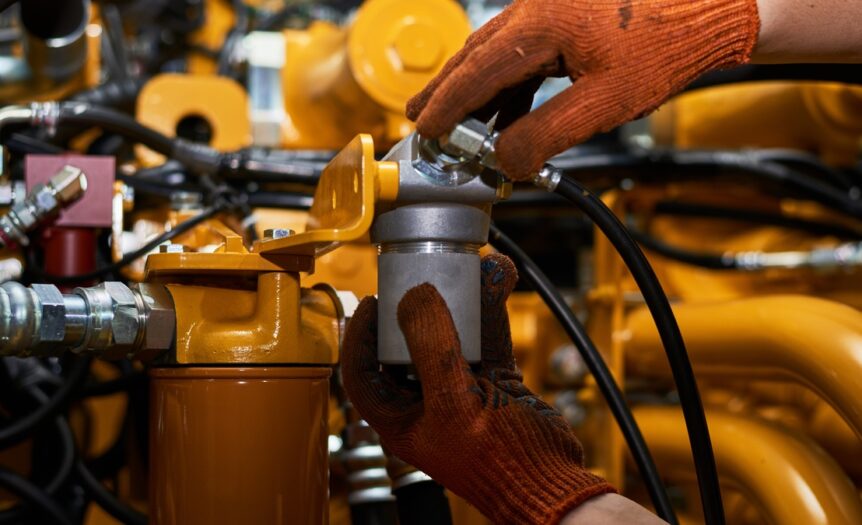
Automobile enthusiasts know the performance of their vehicles depends on maintaining key systems. One often overlooked yet crucial area is the hydraulic system.
Found in brakes, suspensions, and steering systems, hydraulics play a massive role in delivering a smooth, safe, and responsive driving experience. Use this guide to optimize your ride with hydraulic system maintenance.
Understanding Your Vehicle’s Hydraulic Systems
Before jumping into maintenance, it’s important to understand what you’re working with. Hydraulic systems send pressurized fluid through lines and components. This makes it possible to complete tasks like stopping your car, regulating your suspension, or steering precisely. Critical systems include the following:
- brakes that use hydraulic fluid to amplify force applied on the brake pedal to stop your car quickly
- power steering, which helps you effortlessly control your steering wheel with hydraulic assistance
- air- or liquid-based suspension systems that provide comfort by cushioning the ride and adjusting to road conditions
Regular Fluid Checks and Replacement
Hydraulic systems rely on hydraulic fluid to function efficiently. For this reason, keeping it at the right level and condition is key. Check your vehicle manual to locate hydraulic reservoirs, including brake fluid and power steering fluid. Look for these signs while inspecting fluids:
- dark, murky fluid that indicates contamination, as fresh hydraulic fluid is usually clear or amber
- low volume, which may signal a slow leak
- a gritty feel, which suggests it’s time for a flush and replacement
Most manufacturers suggest replacing brake fluid every two years or every 20,000 to 30,000 miles. Still, always follow your car’s maintenance schedule.
Bleeding the Hydraulic Lines
Air in the hydraulic lines can reduce efficiency and cause a spongy brake pedal feel or less responsive steering. Bleeding the system removes trapped air and ensures that pressure transmits correctly. Take these steps to bleed the brakes:
- Locate the bleeder screws near each brake caliper or drum.
- Use a wrench and clear tubing to guide fluid into a container.
- Have someone press the brake pedal while opening each bleeder screw to release air bubbles.
- Close the screw before releasing the pedal, and repeat until air bubbles are gone.
Inspect Hoses, Seals, and Connections
Hydraulic hose maintenance is a must considering how important hoses and seals are to your hydraulic systems. These components can experience wear over time, so regularly inspect for any damage.
Cracks or Leaks
Look for visible fluid drips, damp spots, or bulges in the hoses. These imperfections suggest impending failure.
Loose Connections
Tighten any fittings that show signs of leakage. An adjustment or replacement can prevent costly damages and save you from system failure while driving.
Preventative Care for Longevity
Adopting good habits sustains your hydraulic systems. Avoid overloading your car, which strains the suspension and steering. Likewise, always use the manufacturer-recommended hydraulic fluids. Mixing incompatible types can damage seals and compromise performance.
These upgrades not only optimize your ride with hydraulic system maintenance but also extend the life of these vital systems. Get hands-on, pay close attention to every component, and enjoy the rewards of a better ride.










 Deering Estate
Deering Estate
 Massage Envy South Miami
Massage Envy South Miami
 Calla Blow Dry
Calla Blow Dry
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic
 Sushi Maki
Sushi Maki
 Sports Grill
Sports Grill
 The Healthy Kitchen
The Healthy Kitchen
 Golden Rule Seafood
Golden Rule Seafood
 Malanga Cuban Café
Malanga Cuban Café

 Kathleen Ballard
Kathleen Ballard
 Panter, Panter & Sampedro
Panter, Panter & Sampedro
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 The Dog from Ipanema
The Dog from Ipanema
 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic




 ATR Luxury Homes
ATR Luxury Homes


 2112 Design Studio
2112 Design Studio
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company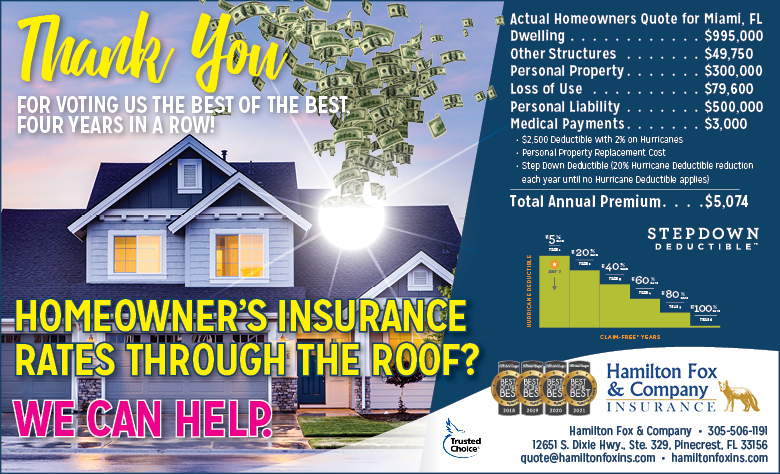
 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services
 Best Pest Professionals
Best Pest Professionals
 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Trinity Air Conditioning Company
Trinity Air Conditioning Company
 Cisca Construction & Development
Cisca Construction & Development
 Mosquito Joe
Mosquito Joe
 Cutler Bay Solar Solutions
Cutler Bay Solar Solutions


 Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
 Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
 Pineview Preschools
Pineview Preschools
 Westminster
Westminster
 Carrollton
Carrollton
 Lil’ Jungle
Lil’ Jungle
 Frost Science Museum
Frost Science Museum
 Palmer Trinity School
Palmer Trinity School
 South Florida Music
South Florida Music
 Pinecrest Orthodontics
Pinecrest Orthodontics
 Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
 d.pediatrics
d.pediatrics
 South Miami Women’s Health
South Miami Women’s Health

 The Spot Barbershop
The Spot Barbershop
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic




 Miami Dance Project
Miami Dance Project

 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic

 Safes Universe
Safes Universe
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 Evenings Delight
Evenings Delight





 Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
 Baptist Health South Florida
Baptist Health South Florida

 Laser Eye Center of Miami
Laser Eye Center of Miami
 Visiting Angels
Visiting Angels
 OpusCare of South Florida
OpusCare of South Florida

 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best





 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company


 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services