Medical sterilization is a critical process in healthcare that ensures the elimination of all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from medical instruments and surfaces. The importance of sterilization cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in preventing infections, ensuring patient safety, and maintaining the integrity of medical procedures.
Let’s look at different types of medical sterilization methods and how they work.
Heat Sterilization
Heat sterilization is the most commonly used method in healthcare facilities. It involves exposing medical equipment or surfaces to high temperatures for a specific period, effectively killing microorganisms. There are two types of heat sterilization: dry heat and moist heat.
Dry Heat Sterilization
In dry heat sterilization, instruments are subjected to high temperatures (usually around 160 degrees Celsius) for an extended period. This process can take anywhere from one hour to several hours, depending on the type of instrument being sterilized. While this method is effective in killing microorganisms, it may not be suitable for items that cannot withstand high temperatures.
Moist Heat Sterilization
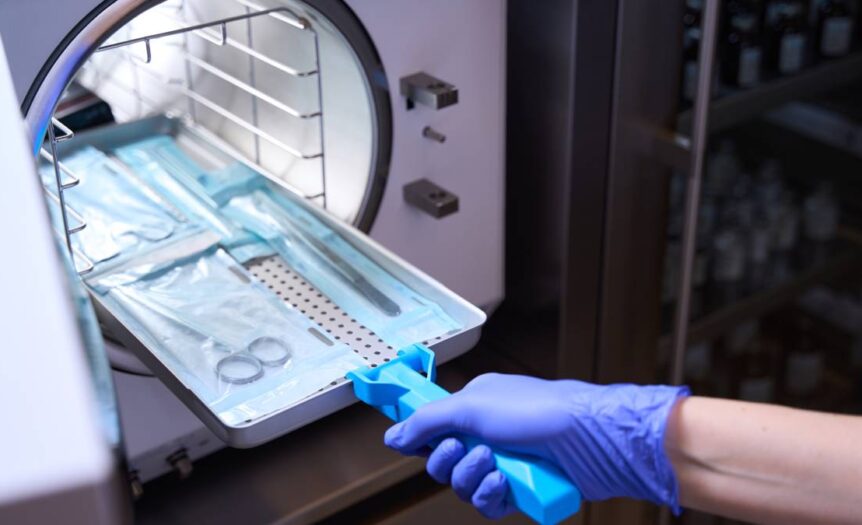
Moist heat sterilization, also known as autoclaving, utilizes steam under pressure to kill microorganisms. The combination of high temperature and pressure makes this method more effective than dry heat sterilization in eliminating various types of microorganisms. Autoclaving is the preferred method for most medical instruments that can withstand high moisture levels.
Chemical Sterilization
Chemical sterilization involves using chemical agents to eliminate microorganisms from equipment or surfaces. This method is useful for heat-sensitive items that cannot be subjected to high temperatures. Some commonly used chemical agents include ethylene oxide, hydrogen peroxide, and glutaraldehyde.
Ethylene Oxide (ETO) Sterilization
ETO sterilization is a popular method of sterilizing medical equipment that cannot withstand high temperatures and moisture. It involves exposing the items to ethylene oxide gas, which has excellent penetration properties, making it effective in killing microorganisms.
Hydrogen Peroxide Sterilization
Hydrogen peroxide sterilization is similar to ETO sterilization, but instead of using gas, it utilizes vaporized hydrogen peroxide. This method is safe and environmentally friendly, as it breaks down into water and oxygen after use.
Radiation Sterilization
Radiation sterilization involves using ionizing radiation (such as gamma rays or electron beams) to eliminate microorganisms from equipment or surfaces. This method is commonly used for single-use medical supplies and devices that cannot withstand high temperatures or moisture.
Filtration Sterilization
Filtration sterilization is a method of removing microorganisms from liquids or gases by passing them through a filter with microscopic pores. This method is useful for heat-sensitive liquids such as medications, vitamins, and certain types of solutions.
Different types of medical sterilization methods are used in healthcare facilities depending on the type of instrument or surface being sterilized. Whether you’re looking into the design of surgical sterilization trays or the proper sterilization of medical devices, understanding the different methods and their effectiveness is crucial in maintaining a safe and sterile environment for patient care.









 Deering Estate
Deering Estate
 Massage Envy South Miami
Massage Envy South Miami
 Calla Blow Dry
Calla Blow Dry
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic
 Sushi Maki
Sushi Maki
 Sports Grill
Sports Grill
 The Healthy Kitchen
The Healthy Kitchen
 Golden Rule Seafood
Golden Rule Seafood
 Malanga Cuban Café
Malanga Cuban Café

 Kathleen Ballard
Kathleen Ballard
 Panter, Panter & Sampedro
Panter, Panter & Sampedro
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 The Dog from Ipanema
The Dog from Ipanema
 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic




 ATR Luxury Homes
ATR Luxury Homes


 2112 Design Studio
2112 Design Studio
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company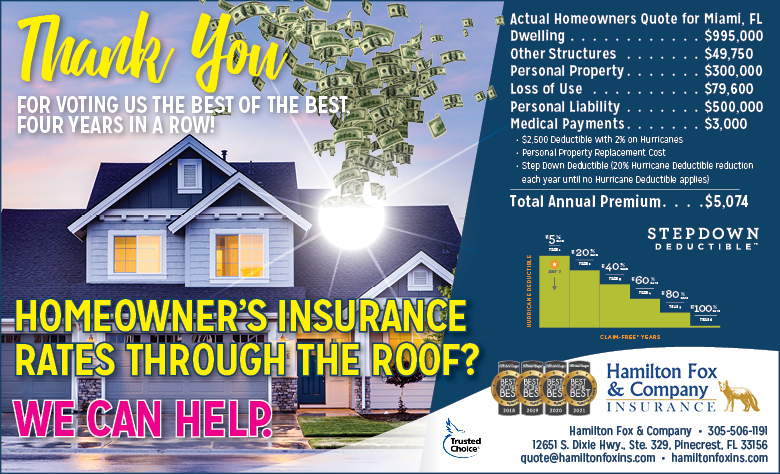
 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services
 Best Pest Professionals
Best Pest Professionals
 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Trinity Air Conditioning Company
Trinity Air Conditioning Company
 Cisca Construction & Development
Cisca Construction & Development
 Mosquito Joe
Mosquito Joe
 Cutler Bay Solar Solutions
Cutler Bay Solar Solutions


 Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
 Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
 Pineview Preschools
Pineview Preschools
 Westminster
Westminster
 Carrollton
Carrollton
 Lil’ Jungle
Lil’ Jungle
 Frost Science Museum
Frost Science Museum
 Palmer Trinity School
Palmer Trinity School
 South Florida Music
South Florida Music
 Pinecrest Orthodontics
Pinecrest Orthodontics
 Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
 d.pediatrics
d.pediatrics
 South Miami Women’s Health
South Miami Women’s Health

 The Spot Barbershop
The Spot Barbershop
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic




 Miami Dance Project
Miami Dance Project

 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic

 Safes Universe
Safes Universe
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 Evenings Delight
Evenings Delight





 Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
 Baptist Health South Florida
Baptist Health South Florida

 Laser Eye Center of Miami
Laser Eye Center of Miami
 Visiting Angels
Visiting Angels
 OpusCare of South Florida
OpusCare of South Florida

 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best





 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company


 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services