While employed as a metalworker, there are several different processes of metal fabrication that you are expected to be familiar with. These common techniques are the foundations of metalworking, and one or more will be utilized in just about every job you encounter.
Casting
Metal casting involves pouring molten metal into a pre-formed mold and then leaving it out to solidify. The most common metals used in this type of fabrication are iron, gold, magnesium, steel, and silver.
Advantages
Several advantages come with casting metal; the main benefit is that it can produce complex shapes with relatively minimal effort when compared to other processes. With the ease in creation also comes a simple post-processing job; metals that are cast need very little alterations after they are made. Metal casting is cheaper than most alternatives when you need to produce large quantities of a design.
Disadvantages
While the process of casting is inexpensive when produced in large quantities, the initial period of mold patterning can be time-consuming and expensive. Due to the mold itself, there’s a limit to the size of the design and the pattern itself, restricting its applications and capabilities.
Shearing
One of the most common processes of metal fabrication, shearing, involves long and straight cuts across sheets of metal to trim them down to the specified size. Shearing is best used with softer metals such as brass, bronze, and aluminum.
Advantages
One of the biggest advantages to metal shearing is that there is nearly no loss of material during the cutting process. Most of the metal can be conserved with virtually none of it going to waste. With the relative simplicity of the process, many sheared metal parts can be produced in a short period of time.
Disadvantages
While it can be used on harder metals, the shearing process has a difficult time cutting through those harder metals. If harder metals are cut, it could cause fracturing in the metal itself and cause increased wear and tear on the shearing tool. Sharing may also produce burrs in the metal. It’s important to remove these burrs before the metal can be considered finished.
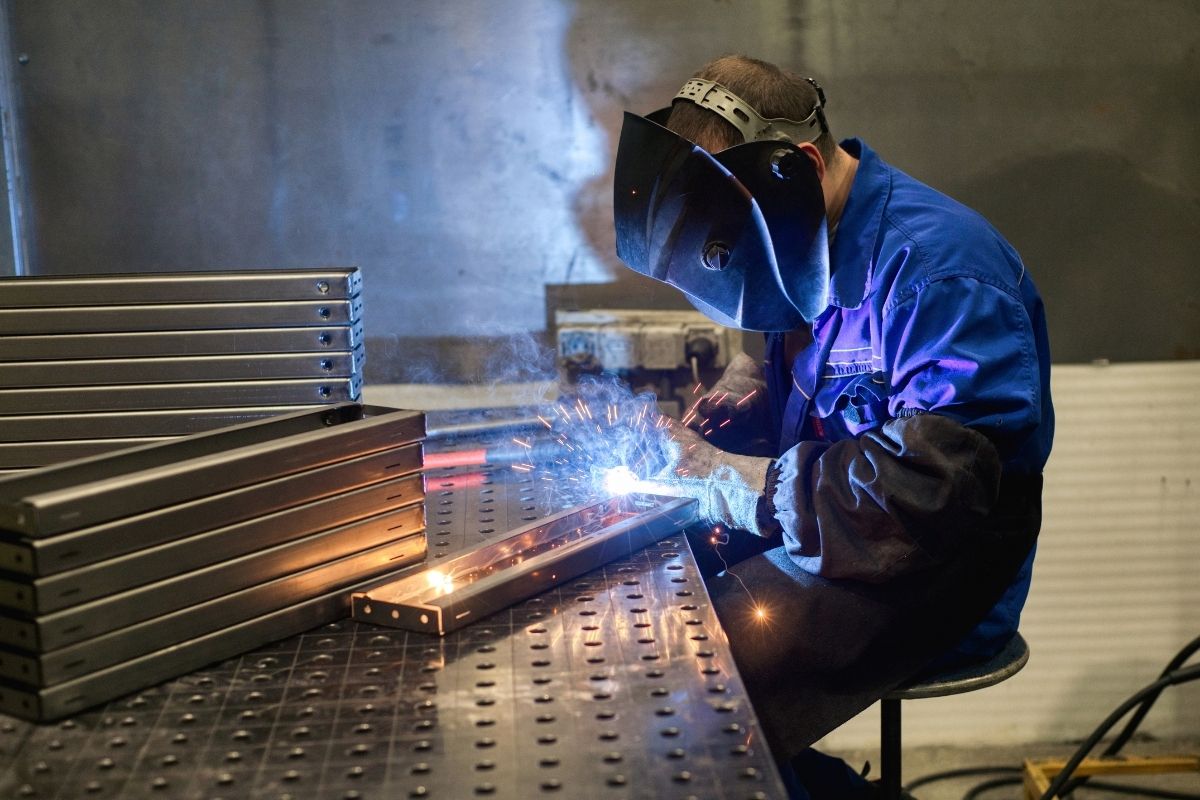
Welding
Welding is the process of joining two metal parts together through the application of heat along the conjoining points of contact.
Advantages
Because two pieces of metal are being attached to each other, there is no extra material to join them. This reduces costs in manufacturing and can cut down on the weight of the final product. Compared to the alternative of riveting joints together, welding is a far less time-consuming process.
Disadvantages
It’s difficult to detect imperfections in the welded joints, such as air bubbles, slag inclusion, and incomplete penetration. The price to properly inspect welding can be costlier than inspecting riveted works. Due to the welding, the joints welded together will be more brittle than the two parent parts that were joined.










 Deering Estate
Deering Estate
 Massage Envy South Miami
Massage Envy South Miami
 Calla Blow Dry
Calla Blow Dry
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic
 Sushi Maki
Sushi Maki
 Sports Grill
Sports Grill
 The Healthy Kitchen
The Healthy Kitchen
 Golden Rule Seafood
Golden Rule Seafood
 Malanga Cuban Café
Malanga Cuban Café

 Kathleen Ballard
Kathleen Ballard
 Panter, Panter & Sampedro
Panter, Panter & Sampedro
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 The Dog from Ipanema
The Dog from Ipanema
 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic




 ATR Luxury Homes
ATR Luxury Homes


 2112 Design Studio
2112 Design Studio
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company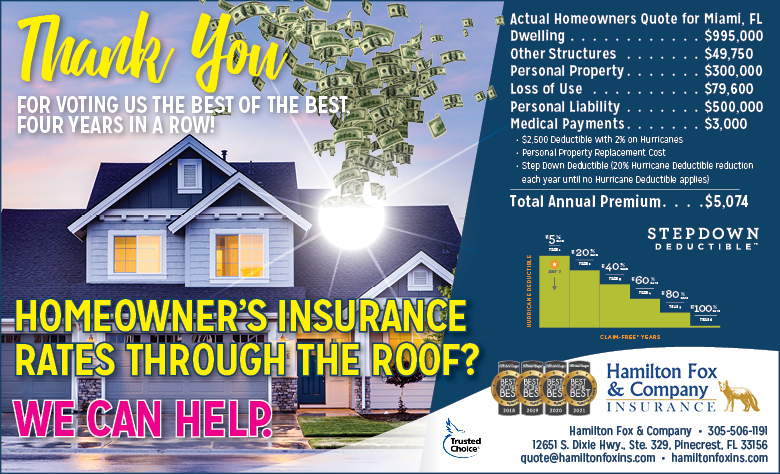
 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services
 Best Pest Professionals
Best Pest Professionals
 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Trinity Air Conditioning Company
Trinity Air Conditioning Company
 Cisca Construction & Development
Cisca Construction & Development
 Mosquito Joe
Mosquito Joe
 Cutler Bay Solar Solutions
Cutler Bay Solar Solutions


 Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
Miami Royal Ballet & Dance
 Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
 Pineview Preschools
Pineview Preschools
 Westminster
Westminster
 Carrollton
Carrollton
 Lil’ Jungle
Lil’ Jungle
 Frost Science Museum
Frost Science Museum
 Palmer Trinity School
Palmer Trinity School
 South Florida Music
South Florida Music
 Pinecrest Orthodontics
Pinecrest Orthodontics
 Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
Dr. Bob Pediatric Dentist
 d.pediatrics
d.pediatrics
 South Miami Women’s Health
South Miami Women’s Health

 The Spot Barbershop
The Spot Barbershop
 My Derma Clinic
My Derma Clinic




 Miami Dance Project
Miami Dance Project

 Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
Rubinstein Family Chiropractic
 Indigo Republic
Indigo Republic

 Safes Universe
Safes Universe
 Vintage Liquors
Vintage Liquors
 Evenings Delight
Evenings Delight





 Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
Atchana’s Homegrown Thai
 Baptist Health South Florida
Baptist Health South Florida

 Laser Eye Center of Miami
Laser Eye Center of Miami
 Visiting Angels
Visiting Angels
 OpusCare of South Florida
OpusCare of South Florida

 Your Pet’s Best
Your Pet’s Best





 HD Tree Services
HD Tree Services
 Hamilton Fox & Company
Hamilton Fox & Company


 Creative Design Services
Creative Design Services